Rel 데이터과학,data_science
Sub
데이터분석,data_analysis - 분석,analysis
{
중요 원리들
}
데이터행렬,data_matrix - 행렬,matrix로 표현,representation하는 것에 대한?
빅데이터,big_data
data_transformation - curr at 변환,transformation - curr name 변환
데이터시스템,data_system or 데이터체계,data
데이터,data
데이터,data
데이터,data
데이터,data
데이터,data
Sub
데이터분석,data_analysis - 분석,analysis
{
중요 원리들
}
데이터행렬,data_matrix - 행렬,matrix로 표현,representation하는 것에 대한?
빅데이터,big_data
data_transformation - curr at 변환,transformation - curr name 변환
데이터시스템,data_system or 데이터체계,data
{
data_acquisition
data acquisition - the process of sampling signals that measure real world physical conditions and converting those samples into digital numeric values that can be used by a computer
data_compression
data compression- the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original data would use
data_encryption
data encryption - the translation of data into a code that allows secure storage or transmission
data_engineering
data engineering - the process of engineering the storage, transmission and processing of data to minimize cost or maximize performance
data_handling
data handling - the process of ensuring that data is stored or disposed of in a secure manner after use
data_processing
data processing - any computer process that summarizes, analyzes or converts data into usable information
data_storage_system
data storage systems - the retention of data in forms not immediately accessible by a CPU, such as hard drives and other devices slower but more permanent than RAM
// via https://ethw.org/Category:Data_systems
}
데이터,datadata_acquisition
data acquisition - the process of sampling signals that measure real world physical conditions and converting those samples into digital numeric values that can be used by a computer
data_compression
data compression- the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original data would use
data_encryption
data encryption - the translation of data into a code that allows secure storage or transmission
data_engineering
data engineering - the process of engineering the storage, transmission and processing of data to minimize cost or maximize performance
data_handling
data handling - the process of ensuring that data is stored or disposed of in a secure manner after use
data_processing
data processing - any computer process that summarizes, analyzes or converts data into usable information
data_storage_system
data storage systems - the retention of data in forms not immediately accessible by a CPU, such as hard drives and other devices slower but more permanent than RAM
// via https://ethw.org/Category:Data_systems
}
데이터,data
데이터,data
데이터,data
데이터,data
데이터,data
Source: ㄷㅎㅈ 2-1
1.1. 수치형 데이터 ¶
데이터가 수치(분명 numerical value ? 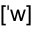 numerical_value x
numerical_value x  Numerical_value x
Numerical_value x 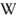 Numerical_value redir to Number ....
Numerical_value redir to Number ....  수치
수치  수치 수,number 값,value)로 되어 있음
수치 수,number 값,value)로 되어 있음
- 연속형 데이터 : 모든 실수값이 가능 // 연속형데이터 연속형자료
- 이산형 데이터 : 특정 값(보통 정수)만 가능 (ex. 문자메시지 수신 횟수) // 이산형데이터 이산형자료
1.2. 범주형 데이터 categorical data ¶
- 데이터가 범주(클래스, 팩터 등)로 되어 있음 // 범주,category 클래스,class, 팩터,factor?
- 명목형 데이터 : 순서가 없음 (ex. 성별, 지역, 오류코드 등)
- 순서형 데이터 : 순서가 있음 (ex. 상/중/하, 등급 등)
1.3. 수치형과 범주형의 구분 ¶
수치형데이터와 범주형데이터의 구분
보면 안다 - 너무 많다면? - 보통은 R이나 Python 데이터 읽는 함수가 고유의 알고리즘으로 판단한다고.
보면 안다 - 너무 많다면? - 보통은 R이나 Python 데이터 읽는 함수가 고유의 알고리즘으로 판단한다고.
대상은 표본,sample? chk
일반적인 판단의 절차
값,value이 문자,character나 기호,symbol의 형태shape? form?
→ 범주형 categorical_data?
숫자 형태인데 겹치는 값이 거의 없을 때→ 수치형 데이터
100개의 표본이 98개의 서로 다른 값을 갖는다? - 98개의 범주를 가질 일은 거의 없으니까 수치형으로 판단.
숫자 형태인데 겹치는 값이 많을 때100개의 표본이 98개의 서로 다른 값을 갖는다? - 98개의 범주를 가질 일은 거의 없으니까 수치형으로 판단.
→ 범주형 데이터에 대한 코드인지 확인 코드인지 확인이 뭔소리? - 아무튼 범주형일 가능성이 상당히 높은 경우임.
100개의 표본이 1과 2 두 개의 값 만을 갖는다
100개의 표본이 1과 2 두 개의 값 만을 갖는다
1.4. 순서-범주형과 이산-수치형은 서로 다름 ¶
- 상/하 vs. 2/1은 수학적으로 유사하게 다룰 수 있음
- 상/중/하 vs. 3/2/1은 불가능
- 일반적으로 서로 구별됨
- 상과 하의 차이는 중과 하의 차이와 같지 않음
- 상과 하의 차이는 중과 하의 차이와 같지 않음
2.2. 범주형 데이터 ¶
- (기초단계) 명목/순서 모두 동일하게 명목형으로 분석
- (고급단계) 순서형 데이터를 순서를 고려하는 방법론을 쓰거나 이산-수치형으로 변환하여 분석
- 변수에 대한 이해가 필요
- 변수에 대한 이해가 필요
2.3. 본 강의에서는 ¶
- 연속-수치형 데이터
 연속-수치형 데이터
연속-수치형 데이터  연속-수치형 데이터
연속-수치형 데이터  연속-수치형 데이터
연속-수치형 데이터
- 명목-범주형 데이터
 명목-범주형 데이터
명목-범주형 데이터  명목-범주형 데이터
명목-범주형 데이터  명목-범주형 데이터
명목-범주형 데이터
로 나누어 살펴볼 예정
3. 수치형 데이터: 대표값 ¶
평균(mean, average) // 평균,mean 평균,average
$\displaystyle \bar{X}=\frac1n\sum_{i=1}^n X_i$
중간값, 중앙값 // 중앙값,median모든 값을 크기 순으로 일렬로 세웠을 때 가운데 있는 값
표본이 짝수 개라면 가장 중간의 두개의 mean을 씀.
최빈값(mode) // 최빈값,mode 모드,mode표본이 짝수 개라면 가장 중간의 두개의 mean을 씀.
4. 수치형 데이터: 분포의 표현 ¶
분포,distribution를 표현하는 값
- 분산,variance or 표준편차,standard_deviation
$\displaystyle S^2=\frac1{n-1}\sum_{i=1}^n (X_i - \bar{X})^2$
- 최대값(max), 최소값(min) // 최대,maximum 최소,minimum 최대값,maximum_value 최소값,minimum_value
- 백분위수(percentile, quantile): 값들은 크기 순으로 일렬로 세웠을 때 하위 %에 해당하는 값
0% percentile ?th quartile 아래에서부터 0%에 해당하는 값 ? 최소값,minimum_value 25% percentile 1st quartile 아래에서부터 25%에 해당하는 값 50% percentile 2nd quartile 아래에서부터 50%에 해당하는 값 / 중앙값,median과 동일. 75% percentile 3rd quartile 아래에서부터 75%에 해당하는 값 100% percentile ?th quartile 아래에서부터 100%에 해당하는 값 ? 최대값,maximum_value
